Blood in Stool – More Than Hemorrhoids, could be Colon Cancer
Center : Gastrointestinal and Liver Center
Article by : Dr. Sombun Rungjiratananon

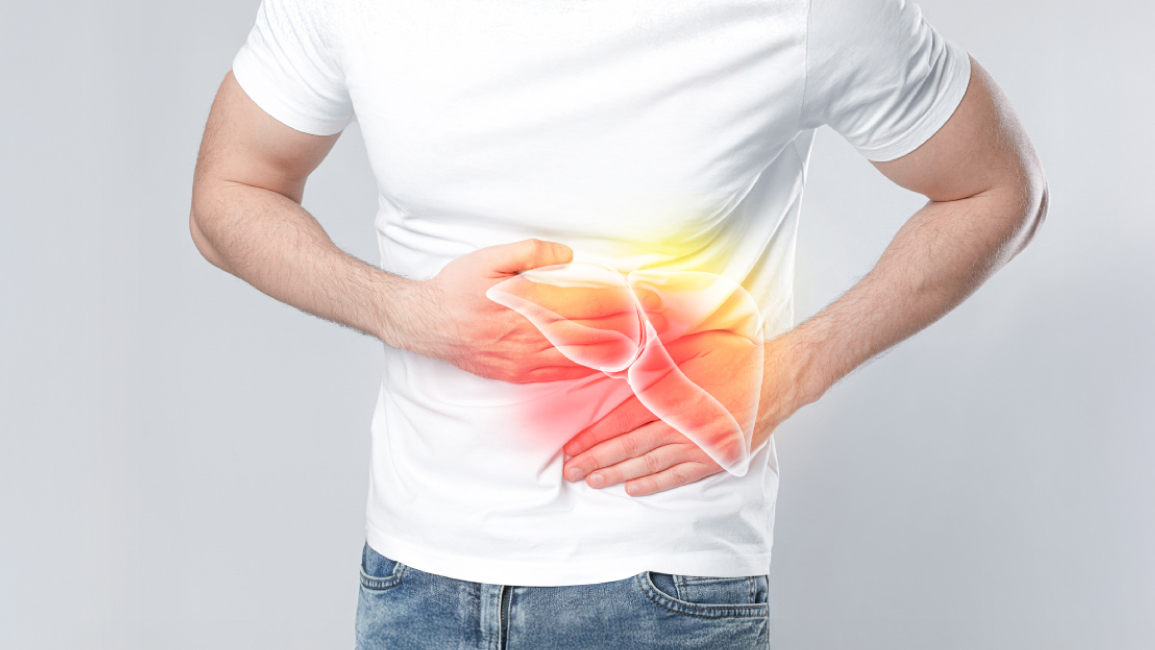
Bowel movements are a normal part of daily life. However, when you notice blood in stool or even slight changes in stool color, it could signal a problem within the digestive system. Many people assume it’s just hemorrhoids, without realizing that this symptom may be an early sign of colon cancer. That’s why it’s important not to ignore it and consult a doctor if it happens to you.
Table of Contents
- What is Blood in Stool?
- Causes of Blood in Stool
- How to recognize signs of gastrointestinal bleeding?
- What does Blood in Stool look like?
- What diseases are related to Blood in Stool?
- Diagnosis and treatment for Blood in Stool
- Prevention of Blood in Stool
- Providing Treatment for Blood in Stool at Nakornthon Hospital
- Free Online Consultation with a Specialist
What is Blood in Stool??


Blood in stool, or hematochezia, refers to the appearance of bright red blood during or after bowel movements. This may include blood-streaked stool, blood clots, or even maroon-colored stool. The causes usually originate from problems in the digestive tract—ranging from the stomach and small intestine to the colon, or from torn veins near the anus. While often mistaken for hemorrhoids, rectal bleeding could indicate something more serious.
Causes of Blood in Stool
Common Causes of Blood in Stool:
- Hemorrhoids The most common cause of blood in stool, hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anus and rectum. Bleeding often occurs during straining or appears as bright red blood on toilet paper.
- Anal Fissures These are small tears in the lining of the anus, typically caused by constipation and passing hard stools. They can cause rectal bleeding along with sharp pain during bowel movements.
- Colitis Inflammation of the colon, which may result from infection or chronic inflammatory conditions such as ulcerative colitis. This can cause bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and urgency.
- Peptic Ulcers Open sores that form on the lining of the stomach or upper small intestine, often due to H. pylori infection. These may lead to maroon stool or darker bleeding if the ulcer is deep.
How to recognize signs of gastrointestinal bleeding?
Observe your stool color daily. Bloody stool or black stool may signal upper digestive issues such as stomach ulcers or small intestine inflammation. If the bleeding comes from the colon, it often appears as bright red blood. In some cases, there may be no visible blood, but symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, or pale complexion may appear—especially in older adults.
What does Blood in Stool look like?
"Blood in stool" is a symptom that should not be overlooked, especially when accompanied by signs like severe abdominal pain, unexpected weight loss, fainting, or fever. These may indicate conditions such as colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, or gastrointestinal ulcers.
- Recurrent or prolonged rectal bleeding that lasts more than 1–2 days
- Large amounts of visible blood in the stool
- Accompanying symptoms like fatigue, fainting, abdominal pain, weight loss, or fever
- Dark or tarry stool, which may indicate bleeding from the stomach or upper intestines (maroon stool vs melena)
- Pre-existing conditions like liver disease, use of blood thinners, or family history of cancer
If bleeding happens only once and no other symptoms are present, monitor it for 1–2 days. But if the stool is black or symptoms worsen, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis.

What diseases are related to Blood in Stool?
Blood in stool can range from a minor issue to a serious health condition. The severity often depends on the amount of blood, frequency, and how long it lasts.
- Stomach bleeding: Often presents with vomiting blood, followed by dark red or almost black stool. It may be a sign of stomach ulcers or even gastric cancer, and symptoms include fatigue or dizziness.
- Colon bleeding: Usually appears as bright red blood or clots in stool without anal pain, often caused by conditions affecting the colon lining.
- Ischemic colitis: When blood supply to the colon is restricted, it causes tissue damage. If bloody stool occurs with abdominal cramps, fainting, or sepsis risk, it’s a medical emergency.
- Colon polyps: These benign growths can bleed occasionally and may develop into colon cancer if not treated.
- Colon cancer: One of the leading causes of cancer death. Symptoms include constipation, diarrhea, blood in stool, black stool, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss.
Diagnosis and treatment for Blood in Stool
Since there are various causes of blood in stool, treatment depends on the severity of the condition:
1. Mild bleeding Often due to constipation or minor tears. Eating a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and maintaining bowel habits can help relieve symptoms.
2. Heavy bleeding If bleeding is frequent or heavy, medical attention is required. Doctors may conduct stool tests or a colonoscopy to find the cause and provide appropriate treatment.
Colonoscopy in the diagnosis of Blood in Stool
A colonoscopy is an important diagnostic tool that helps locate the cause of gastrointestinal bleeding. It uses a thin tube with a camera to inspect the colon and rectum. Doctors can collect tissue samples, detect early signs of colon cancer, or remove abnormal growths during the procedure. You should consider a colonoscopy if you experience:
- Chronic bloating or abdominal pain
- Alternating constipation and diarrhea
- Blood in stool or narrow-shaped stool
- Loss of appetite or unexplained weight loss
Treatment for Blood in Stool
- Warm sitz baths can relieve discomfort caused by hemorrhoids or anal tears
- Endoscopic treatment: Bleeding can be stopped by injecting substances or using clips/lasers via colonoscopy
- Medications: Antibiotics for infections or anti-inflammatory drugs for conditions like colitis
- Surgery: Required in severe cases, such as polyp removal or cancer surgery
Prevention of Blood in Stool
There are several lifestyle habits that can help prevent blood in stool and maintain digestive health:
- Drink at least 8–10 glasses of water daily to support regular bowel movements
- Eat a high-fiber diet with plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, and seeds
- Exercise regularly to stimulate digestion and prevent constipation
- Don’t delay bowel movements—train your body to have regular toilet habits
- Avoid foods that irritate the stomach, such as spicy, greasy, or overly processed items
- Adults aged 45 and older should consider a colonoscopy to screen for colon polyps or cancer
- Quit smoking—smoking increases the risk of many cancers, including colon cancer
Manage chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, which can affect blood vessels and digestive function
Providing Treatment for Blood in Stool at Nakornthon Hospital
If you notice blood in stool or related symptoms, don’t delay. Early diagnosis can prevent serious outcomes. At Nakornthon Hospital’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Center, we offer full diagnostic and treatment services—including colonoscopy, lab tests, and recovery facilities—all under one roof for your convenience and safety. We provide comprehensive one-stop services for diagnosis and treatment of various diseases, including liver cancer—all conveniently located in one place.
For more information, please contact:
- - Website : https://en.nakornthon.com
- - Facebook : Nakornthon Hospital - International Patient
- - Line : @nakornthoninter
- - Tel: 02-450-9999 (Available 24 hours)
Free Online Consultation
Article of Gastrointestinal and Liver Center